In the next 7 years, Georgia intends to increase almond production by at least 16 times. Almonds are not the main ingredient in Georgian cuisine and there are no production facilities actively using almonds as raw material, which is reflected in the low consumption of nuts. Therefore, now we need to think about the prospects for the export of nuts.
According to the Georgian Almond and Walnut Producers Association (AWPA), the harvest of almonds from the currently operating orchards is projected at 14 thousand tons (in shell) in 2027. This is a significant increase when compared to about 0.9 thousand tons in 2019-2020.
Over the past 20 years, the supply of almond kernels (production and imports minus exports) has grown at a slow pace, with an increase of about 9 tons per year. There is no clear upward trend in the past 7 years, however, these recent trends are expected to change very quickly.
AWPA warns of an increase in almond production in Georgia. According to the forecast of the association, almond production in Georgia will grow by an average of 48% per year from 2020 to 2027, excluding new orchards established after 2020. The total harvest by 2027 will be a record high, at least 14 times higher than the current harvest and at least 17 times higher than the 2001-2019 average.
The almond sector of Georgia has a lot of work to do in order to be successful both in export and supply to the local market. There are virtually no major players in the post-harvest supply chain, and local consumption of almonds is so low that they cannot utilize these volumes. If all these new almonds are not exported, but consumed locally, Georgia will be among the top three per capita consumers of almonds by 2027. This seems impossible at the moment. The low consumption of almonds in Georgia is associated with both the local consumption culture, and the income of the population.
According to EastFruit analysts estimates, per capita consumption of almonds (kernels) in Georgia was typically in the range of 0.08-0.11 kg per year in 2016-2020. According to the International Nuts and Dried Fruit Council (INC), the 16 countries with the highest consumption consume an average of 7-8 times more per capita. In these countries, the average GDP per capita is $ 35,000, while that of Georgia is $ 4,400 (source: World Bank). Thus, the overall economic growth of the country is likely to be critical to the growth of local consumption of almonds.
If the current structure of local consumption does not change, Georgia will have to export about 300 tons of almond kernels in 2021 and over 5,000 tons in 2027.
Given the expected volumes, Georgia should pay attention to the developments on the global market. Typically, the global trade value of almond kernels is about 4 times higher than that of in-shell almonds. The leaders are the United States (70% of world exports of almond kernels – 629 thousand tons of kernels in 2020), Spain (94 thousand tons) and Australia (56 thousand tons). These countries offer high quality processed nuts in large quantities.
Notably, it was the overproduction of almonds in the United States that caused the most recent sharp drop in world prices in 2020.
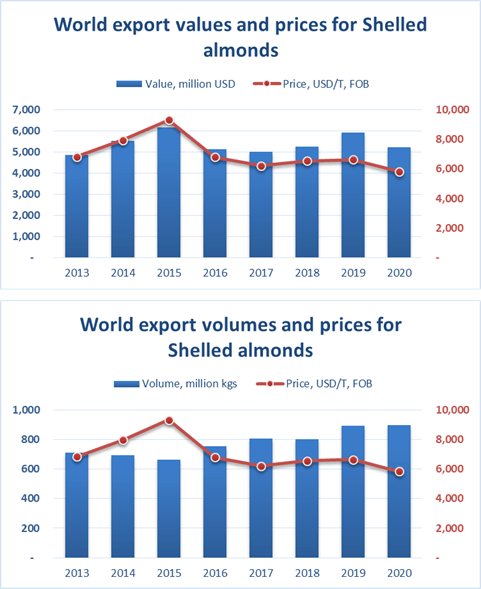
Source: TradeMap.org
Read also: Fears are confirmed – the prices for nuts in the USA are steadily creeping down (RU)
The list of importers of in-shell almonds is very concentrated. In 2020, the largest importer, India, imported twice as much as the other 9 largest importers combined.
The trade in almond kernels is more active and varied. The right move would be to focus on exporting kernels rather than in-shell almonds.
Top importers of almond kernels in 2020
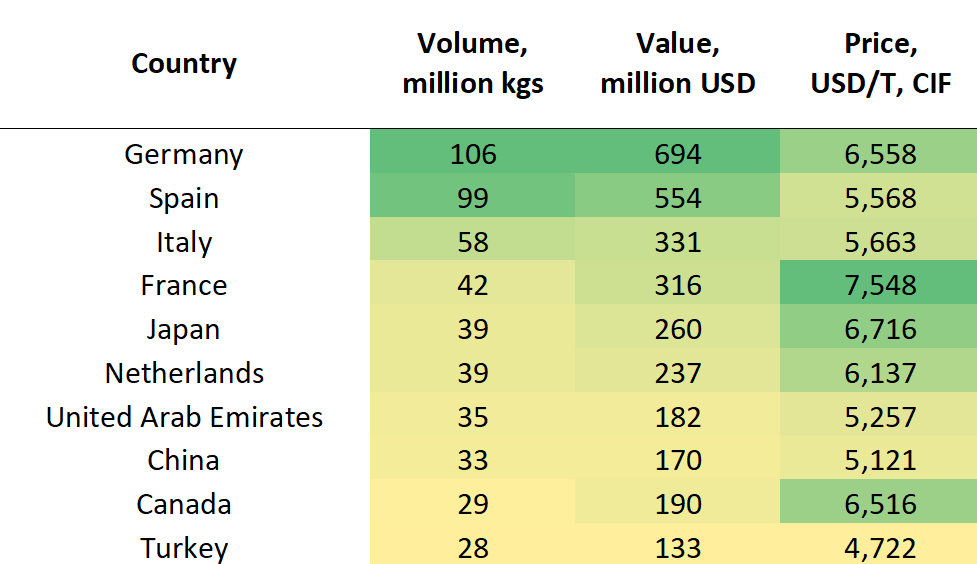
Source: TradeMap.org
Europe is considered to be the main importing market with higher prices and higher import volumes. A free trade agreement between Georgia and the EU, as well as the links established through the hazelnut trade, can be beneficial. But the EU, where more than half of the almond kernels are consumed as snacks, has high nut quality standards and controls pesticide residues and aflatoxin levels. Therefore, post-harvest handling and storage of the almonds will be critical.Source: TradeMap.orgTop importers of almond kernels in 2020
China can also be Georgia’s target. Imports of almond kernels to China increased by more than 650% (2020 compared to 2013-2015). The average price is close to the European one ($ 5121 per ton), and the growth in imports is the highest for countries that imported more than 16 million kilograms of almond kernels in 2020.
It is good that Georgian almond growers are aware that most of their products should be exported. According to the AWPA, large volumes of almonds are coming soon, but so far we do not see channels large enough for the expected almond production to be traded through. As the significant development in post-harvest handling is needed, maybe now is the best time to start an almond processing business in Georgia.
The use of the site materials is free if there is a direct and open for search engines hyperlink to a specific publication of the East-Fruit.com website.




